Introduction
应用层可以使用内核提供的文件系统通知API来获取文件系统中发生的变化,比如打开、关闭、创建、删除文件(夹)等。内核最开始在2.4.0中实现了dnotify,但dnotify重用了fcntl系统调用,有很多问题,比如:(1)dnotify只能监控文件夹,不能监控某个文件;(2)使用信号SIGIO来向进程传递事件,但信号是异步的,可能丢失,而且传递的信息太少,比如,无法知道到底是文件夹的哪个文件发生的事件。
后面,内核在2.6.13实现了inotify,inotify实现了几个新的系统调用,解决了dnotify的问题。
- inotifywait
我们可以使用inotify-tools中自带的inotifywait来监控某个目录的事件。
#inotifywait -rme modify,open,create,delete,close /root/dbyin/test/
Setting up watches. Beware: since -r was given, this may take a while!
Watches established.
/root/dbyin/test/ CREATE f1.txt
/root/dbyin/test/ OPEN f1.txt
/root/dbyin/test/ MODIFY f1.txt
/root/dbyin/test/ CLOSE_WRITE,CLOSE f1.txt
/root/dbyin/test/ DELETE f1.txt
Another terminal:
#echo hello > /root/dbyin/test/f1.txt
#rm /root/dbyin/test/f1.txt
程序示例参考这里
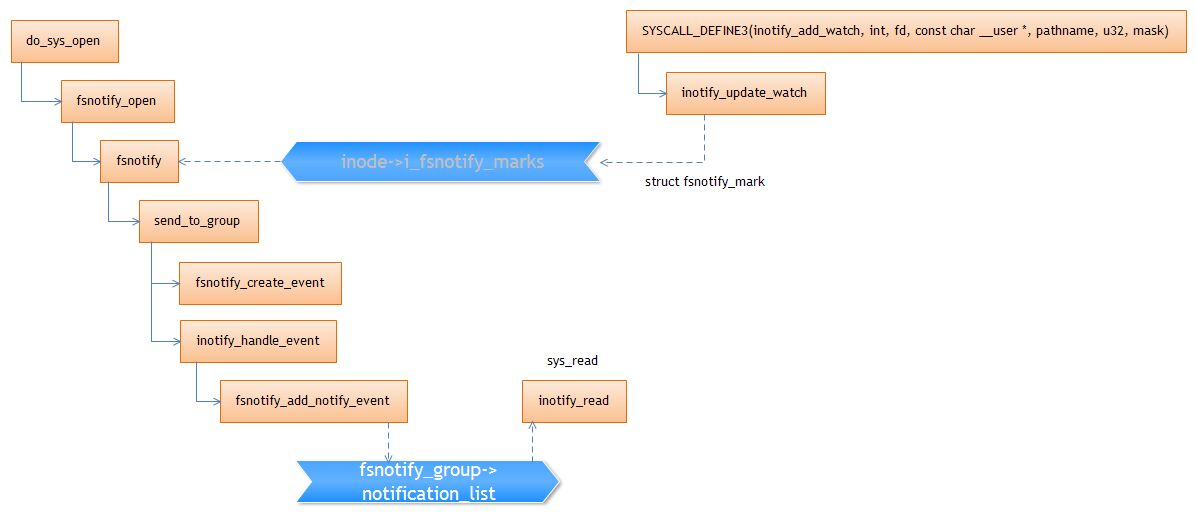
Inotify的实现
核心数据结构
- fsnotify_group
fsnotify_group代表一个inotify实例,每次应用层调用inotify_init就会创建一个实例,它维护该实例的所有event信息:
/*
* A group is a "thing" that wants to receive notification about filesystem
* events. The mask holds the subset of event types this group cares about.
* refcnt on a group is up to the implementor and at any moment if it goes 0
* everything will be cleaned up.
*/
struct fsnotify_group {
const struct fsnotify_ops *ops; /* how this group handles things, inotify_fops */
struct list_head notification_list; /* list of event_holder this group needs to send to userspace, fsnotify_event list */
wait_queue_head_t notification_waitq; /* read() on the notification file blocks on this waitq */
unsigned int q_len; /* events on the queue */
unsigned int max_events; /* maximum events allowed on the list */
struct list_head marks_list; /* all inode marks for this group, struct fsnotify_mark list */
struct fasync_struct *fsn_fa; /* async notification */
/* groups can define private fields here or use the void *private */
union {
void *private;
#ifdef CONFIG_INOTIFY_USER
struct inotify_group_private_data {
spinlock_t idr_lock;
struct idr idr; ///id -> inotify_inode_mark*
struct user_struct *user;
} inotify_data; ///for inotify
#endif
}
}
- fsnotify_mark
fsnotify_mark是联系fsnotify_group与inode的桥梁,fsnotify_group->marks_list为fsnotify_mark链表,fsnotify_mark.i->inode指向被监听文件的inode。inode->i_fsnotify_marks保存监听该inode的所有inotify实例。
struct inotify_inode_mark {
struct fsnotify_mark fsn_mark;
int wd; ///watch descriptor
};
struct fsnotify_mark {
__u32 mask; /* mask this mark is for */
/* we hold ref for each i_list and g_list. also one ref for each 'thing'
* in kernel that found and may be using this mark. */
atomic_t refcnt; /* active things looking at this mark */
struct fsnotify_group *group; /* group this mark is for */
struct list_head g_list; /* list of marks by group->i_fsnotify_marks */
spinlock_t lock; /* protect group and inode */
union {
struct fsnotify_inode_mark i;
struct fsnotify_vfsmount_mark m;
};
__u32 ignored_mask; /* events types to ignore */
#define FSNOTIFY_MARK_FLAG_INODE 0x01
#define FSNOTIFY_MARK_FLAG_VFSMOUNT 0x02
#define FSNOTIFY_MARK_FLAG_OBJECT_PINNED 0x04
#define FSNOTIFY_MARK_FLAG_IGNORED_SURV_MODIFY 0x08
#define FSNOTIFY_MARK_FLAG_ALIVE 0x10
unsigned int flags; /* vfsmount or inode mark? */
struct list_head destroy_list;
void (*free_mark)(struct fsnotify_mark *mark); /* called on final put+free */
};
/*
* Inode specific fields in an fsnotify_mark
*/
struct fsnotify_inode_mark {
struct inode *inode; /* inode this mark is associated with */
struct hlist_node i_list; /* list of marks by inode->i_fsnotify_marks */
struct list_head free_i_list; /* tmp list used when freeing this mark */
};
- inode and file
/*
* Keep mostly read-only and often accessed (especially for
* the RCU path lookup and 'stat' data) fields at the beginning
* of the 'struct inode'
*/
struct inode {
#ifdef CONFIG_FSNOTIFY
__u32 i_fsnotify_mask; /* all events this inode cares about */
struct hlist_head i_fsnotify_marks; ///struct fsnotify_inode_mark list, see fsnotify_inode_mark.i_list
#endif
}
struct file {
///...
void *private_data; ///fsnotify_group*
}
Overlayfs的实现
- 数据结构
Overlayfs的几个关键数据结构:
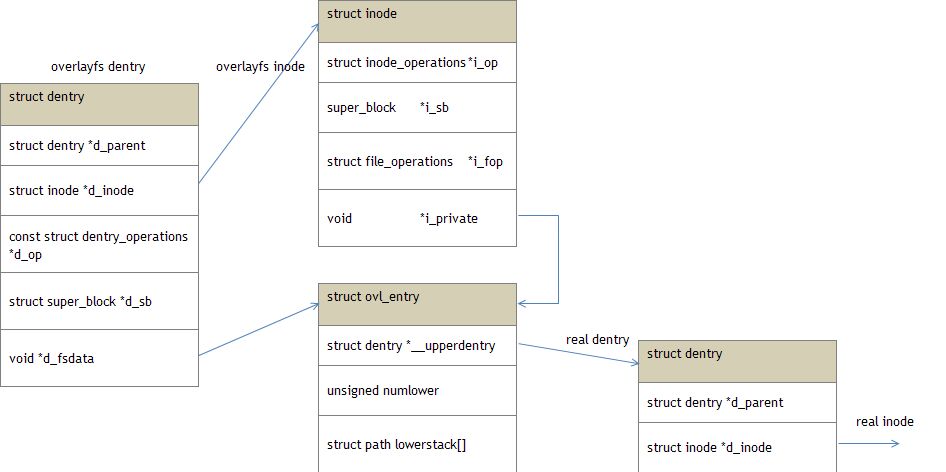
struct dentry {
struct dentry *d_parent; /* parent directory,父目录dentry对象 */
struct qstr d_name; ///当前分量的名称
struct inode *d_inode; /* inode对象, create by ovl_new_inode */
const struct dentry_operations *d_op; /// == super_block->s_d_op == ovl_dentry_operations
struct super_block *d_sb; /* The root of the dentry tree */
void *d_fsdata; /* fs-specific data, struct ovl_entry */
}
/* private information held for every overlayfs dentry */
struct ovl_entry {
struct dentry *__upperdentry; ///not NULL if got in upperdir
struct ovl_dir_cache *cache;
union {
struct {
u64 version;
bool opaque;
};
struct rcu_head rcu;
};
unsigned numlower;
struct path lowerstack[]; ///not NULL if got in lowdir
};
struct inode {
const struct inode_operations *i_op; ///ovl_dir_inode_operations
struct super_block *i_sb;
const struct file_operations *i_fop; /* former ->i_op->default_file_ops, ovl_dir_operations */
void *i_private; /* fs or device private pointer, struct ovl_entry*/
};
dentry是内核的目录项对象,每个目录(文件)都有一个对应的对象,对于overlayfs的每个dentry的指向的inode并没有实际的磁盘数据,而是由ovl_new_inode创建的一个内存inode;dentry->d_fsdata指向ovl_entry,而后者指向真正的underlay fs的dentry。
在overlayfs遍历时,dentry->inode并没有多大用,实际上,在ovl_lookup中,代表父目录的inode参数struct inode *dir并没有没使用到。而dentry->d_fsdata指向ovl_entry才是进行查找的关键因素,通过ovl_entry进入到underlay fs的查找。
///dir: parent directory inode object, dentry: dentry object for current finding dircotry entry
struct dentry *ovl_lookup(struct inode *dir, struct dentry *dentry,
unsigned int flags) ///called by lookup_real
{
struct ovl_entry *oe;
struct ovl_entry *poe = dentry->d_parent->d_fsdata; ///dentry->d_parent->d_inode == dir
struct path *stack = NULL;
struct dentry *upperdir, *upperdentry = NULL;
unsigned int ctr = 0;
struct inode *inode = NULL;
bool upperopaque = false;
struct dentry *this, *prev = NULL;
unsigned int i;
int err;
upperdir = ovl_upperdentry_dereference(poe);
if (upperdir) { ///(1)lookup in upperdir firstly
this = ovl_lookup_real(upperdir, &dentry->d_name);
err = PTR_ERR(this);
if (IS_ERR(this))
goto out;
if (this) {///exist in upperdir
if (unlikely(ovl_dentry_remote(this))) {
dput(this);
err = -EREMOTE;
goto out;
}
if (ovl_is_whiteout(this)) {
dput(this); ///whiteout file
this = NULL;
upperopaque = true;
} else if (poe->numlower && ovl_is_opaquedir(this)) {
upperopaque = true; ///opaque dir
}
}
upperdentry = prev = this;
}
///(2)didn't find dentry in upperdir
if (!upperopaque && poe->numlower) {
err = -ENOMEM;
stack = kcalloc(poe->numlower, sizeof(struct path), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!stack)
goto out_put_upper;
}
///(3)find dentry in lowdir
for (i = 0; !upperopaque && i < poe->numlower; i++) {
bool opaque = false;
struct path lowerpath = poe->lowerstack[i];
this = ovl_lookup_real(lowerpath.dentry, &dentry->d_name);
err = PTR_ERR(this);
if (IS_ERR(this)) {
/*
* If it's positive, then treat ENAMETOOLONG as ENOENT.
*/
if (err == -ENAMETOOLONG && (upperdentry || ctr))
continue;
goto out_put;
}
if (!this)
continue;
if (ovl_is_whiteout(this)) {
dput(this);
break;
}
/*
* Only makes sense to check opaque dir if this is not the
* lowermost layer.
*/
if (i < poe->numlower - 1 && ovl_is_opaquedir(this))
opaque = true;
if (prev && (!S_ISDIR(prev->d_inode->i_mode) ||
!S_ISDIR(this->d_inode->i_mode))) {
/*
* FIXME: check for upper-opaqueness maybe better done
* in remove code.
*/
if (prev == upperdentry)
upperopaque = true;
dput(this);
break;
}
/*
* If this is a non-directory then stop here.
*/
if (!S_ISDIR(this->d_inode->i_mode))
opaque = true;
stack[ctr].dentry = this;
stack[ctr].mnt = lowerpath.mnt;
ctr++;
prev = this;
if (opaque)
break;
}
oe = ovl_alloc_entry(ctr); ///ovl_dentry for current finding dentry
err = -ENOMEM;
if (!oe)
goto out_put;
if (upperdentry || ctr) {///if got in upperdir, upperdentry != NULL; else if got in lowdir, ctr > 0
struct dentry *realdentry;
realdentry = upperdentry ? upperdentry : stack[0].dentry;
///alloc overlayfs inode for current real inode
err = -ENOMEM;
inode = ovl_new_inode(dentry->d_sb, realdentry->d_inode->i_mode,
oe);
if (!inode)
goto out_free_oe;
ovl_copyattr(realdentry->d_inode, inode);
}
oe->opaque = upperopaque;
oe->__upperdentry = upperdentry;
memcpy(oe->lowerstack, stack, sizeof(struct path) * ctr);
kfree(stack);
dentry->d_fsdata = oe; ///ovl_entry
d_add(dentry, inode);
return NULL;
out_free_oe:
kfree(oe);
out_put:
for (i = 0; i < ctr; i++)
dput(stack[i].dentry);
kfree(stack);
out_put_upper:
dput(upperdentry);
out:
return ERR_PTR(err);
}
- open and copy up
overlayfs在打开文件时,会让struct file->f_inode指向real inode;而且,如果会修改文件,且upperdir不存在该文件,则会从lowerdir进行copy up:
int vfs_open(const struct path *path, struct file *file,
const struct cred *cred)
{
struct dentry *dentry = path->dentry; ///overlayfs dentry
struct inode *inode = dentry->d_inode; ///overlayfs inode
file->f_path = *path;
if (dentry->d_flags & DCACHE_OP_SELECT_INODE) {
inode = dentry->d_op->d_select_inode(dentry, file->f_flags); ///get real inode, ovl_dentry_operations
if (IS_ERR(inode))
return PTR_ERR(inode);
}
return do_dentry_open(file, inode, NULL, cred); ///file->f_inode = inode
}
///return underlay fs inode
struct inode *ovl_d_select_inode(struct dentry *dentry, unsigned file_flags)
{
int err;
struct path realpath;
enum ovl_path_type type;
if (S_ISDIR(dentry->d_inode->i_mode))
return dentry->d_inode;
type = ovl_path_real(dentry, &realpath); ///real dentry
if (ovl_open_need_copy_up(file_flags, type, realpath.dentry)) { ///need copy up
err = ovl_want_write(dentry);
if (err)
return ERR_PTR(err);
if (file_flags & O_TRUNC)
err = ovl_copy_up_truncate(dentry);
else
err = ovl_copy_up(dentry); ///copy up
ovl_drop_write(dentry);
if (err)
return ERR_PTR(err);
ovl_path_upper(dentry, &realpath);
}
if (realpath.dentry->d_flags & DCACHE_OP_SELECT_INODE)
return realpath.dentry->d_op->d_select_inode(realpath.dentry, file_flags);
return realpath.dentry->d_inode; ///return real inode
}
Inotify and Overlayfs
inotify_add_watch使用的是overlayfs inode:
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(inotify_add_watch, int, fd, const char __user *, pathname,
u32, mask)
{
///...
ret = inotify_find_inode(pathname, &path, flags); ///返回overlayfs inode
if (ret)
goto fput_and_out;
/* inode held in place by reference to path; group by fget on fd */
inode = path.dentry->d_inode; ///monitored file(overlay inode)
group = f.file->private_data; ///notify group
/* create/update an inode mark */
ret = inotify_update_watch(group, inode, mask);
///...
}
fsnotify_open使用的是underlayfs inode:
/*
* fsnotify_open - file was opened
*/
static inline void fsnotify_open(struct file *file)
{
struct path *path = &file->f_path;
struct inode *inode = file_inode(file); ///for overlayfs , after vfs_open, f->f_inode == underlay inode
__u32 mask = FS_OPEN;
if (S_ISDIR(inode->i_mode))
mask |= FS_ISDIR;
fsnotify_parent(path, NULL, mask);
fsnotify(inode, mask, path, FSNOTIFY_EVENT_PATH, NULL, 0);
}
在vfs_open中,内核会将file->f_inode指向underlayfs inode:
int vfs_open(const struct path *path, struct file *file,
const struct cred *cred)
{
struct dentry *dentry = path->dentry; ///overlayfs dentry
struct inode *inode = dentry->d_inode; ///overlayfs inode
file->f_path = *path;
if (dentry->d_flags & DCACHE_OP_SELECT_INODE) {
inode = dentry->d_op->d_select_inode(dentry, file->f_flags); ///get underlayfs inode, ovl_dentry_operations
if (IS_ERR(inode))
return PTR_ERR(inode);
}
return do_dentry_open(file, inode, NULL, cred); ///file->f_inode = inode
}
所以,对单个文件进行watch时,无法得到事件。