OVS的流表原理
OVS中的flow cache分两级:microflow cache和megaflow cache。前者用于精确匹配(exact matching),即用skb_buff->skb_hash进行匹配;后者用于通配符匹配(wildcard matching),使用元组空间搜索算法实现,即tuple space search (TSS) .
TSS
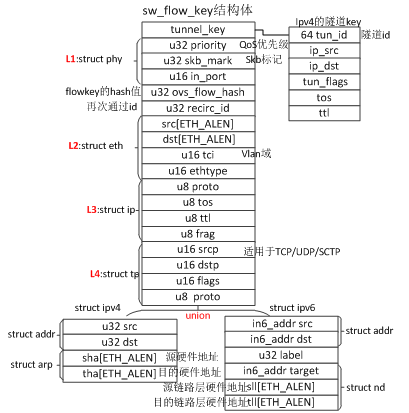
OVS使用sw_flow_key进行流匹配,字段比较多,包含L1到L4协议的关键信息:
那么为什么OVS选择TSS,而不选择其他查找算法?这里给出了以下三点解释:
- (1)在虚拟化数据中心环境下,流的添加删除比较频繁,TSS支持高效的、常数时间的表项更新;
- (2)TSS支持任意匹配域的组合;
- (3)TSS存储空间随着流的数量线性增长。
OVS流表的实现
///mask cache entry
struct mask_cache_entry {
u32 skb_hash;
u32 mask_index; /// mask index in flow_table->mask_array->masks
};
struct mask_array {
struct rcu_head rcu;
int count, max;
struct sw_flow_mask __rcu *masks[]; /// mask array
};
struct table_instance { /// hash table
struct flex_array *buckets; ///bucket array
unsigned int n_buckets;
struct rcu_head rcu;
int node_ver;
u32 hash_seed;
bool keep_flows;
};
struct flow_table {
struct table_instance __rcu *ti; ///hash table
struct table_instance __rcu *ufid_ti;
struct mask_cache_entry __percpu *mask_cache; ///microflow cache, find entry by skb_hash, 256 entries(MC_HASH_ENTRIES)
struct mask_array __rcu *mask_array; ///mask array
unsigned long last_rehash;
unsigned int count;
unsigned int ufid_count;
};
struct flow_table对应datapath的流表,它主要包括3部分:
- (1) ti
ti为流表对应的hash表,典型的哈希桶+链表的实现。hash表中的元素为sw_flow,它表示一个流表项:
/// flow table entry
struct sw_flow {
struct rcu_head rcu;
struct {
struct hlist_node node[2];
u32 hash;
} flow_table, ufid_table; /// hash table node
int stats_last_writer; /* CPU id of the last writer on
* 'stats[0]'.
*/
struct sw_flow_key key; ///key
struct sw_flow_id id;
struct cpumask cpu_used_mask;
struct sw_flow_mask *mask;
struct sw_flow_actions __rcu *sf_acts; ///action
struct flow_stats __rcu *stats[]; /* One for each CPU. First one
* is allocated at flow creation time,
* the rest are allocated on demand
* while holding the 'stats[0].lock'.
*/
};
- (2) mask_cache
mask_cache为microflow cache,用于精确匹配(EMC)。它是percpu数组,有256个元素,即mask_cache_entry。
mask_cache_entry 有2个字段:skb_hash用于与skb_buff->skb_hash比较;mask_index为对应的sw_flow_mask在mask_array数组中的下标。
- (3) mask_array
mask_array为sw_flow_mask数组,每个sw_flow_mask表示一个掩码(Mask),用于指示sw_flow_key中的哪些字段需要进行匹配:
Each bit of the mask will be set to 1 when a match is required on that bit position; otherwise, it will be 0.
struct sw_flow_key_range {
unsigned short int start;
unsigned short int end;
};
/// flow mask
struct sw_flow_mask {
int ref_count;
struct rcu_head rcu;
struct sw_flow_key_range range;
struct sw_flow_key key;
};
流表查找过程
流表查找的目标是基于skb_buff创建一个sw_flow_key,在流表中找到匹配的流表项sw_flow。
ovs_flow_tbl_lookup_stats是进行入流表查找的入口函数,参数包括流表对象、用于匹配的sw_flow_key、和用于精确匹配的skb_hash:
/*
* mask_cache maps flow to probable mask. This cache is not tightly
* coupled cache, It means updates to mask list can result in inconsistent
* cache entry in mask cache.
* This is per cpu cache and is divided in MC_HASH_SEGS segments.
* In case of a hash collision the entry is hashed in next segment.
*/
struct sw_flow *ovs_flow_tbl_lookup_stats(struct flow_table *tbl,
const struct sw_flow_key *key,
u32 skb_hash,
u32 *n_mask_hit)
{
struct mask_array *ma = rcu_dereference(tbl->mask_array);
struct table_instance *ti = rcu_dereference(tbl->ti);
struct mask_cache_entry *entries, *ce;
struct sw_flow *flow;
u32 hash;
int seg;
*n_mask_hit = 0;
if (unlikely(!skb_hash)) {
u32 mask_index = 0;
return flow_lookup(tbl, ti, ma, key, n_mask_hit, &mask_index);
}
/* Pre and post recirulation flows usually have the same skb_hash
* value. To avoid hash collisions, rehash the 'skb_hash' with
* 'recirc_id'. */
if (key->recirc_id)
skb_hash = jhash_1word(skb_hash, key->recirc_id);
ce = NULL;
hash = skb_hash;
entries = this_cpu_ptr(tbl->mask_cache);
/* Find the cache entry 'ce' to operate on. */
for (seg = 0; seg < MC_HASH_SEGS; seg++) { ///find in cache
int index = hash & (MC_HASH_ENTRIES - 1); ///skb_hash -> index
struct mask_cache_entry *e;
e = &entries[index];
if (e->skb_hash == skb_hash) {
flow = flow_lookup(tbl, ti, ma, key, n_mask_hit,
&e->mask_index);
if (!flow)
e->skb_hash = 0;
return flow;
}
if (!ce || e->skb_hash < ce->skb_hash)
ce = e; /* A better replacement cache candidate. */
hash >>= MC_HASH_SHIFT;
}
/* Cache miss, do full lookup. */
flow = flow_lookup(tbl, ti, ma, key, n_mask_hit, &ce->mask_index);
if (flow)
ce->skb_hash = skb_hash;
return flow;
}
可以看到,ovs_flow_tbl_lookup_stats会先尝试使用skb_hash查找mask_cache_entry。如果成功,则将mask_index传给flow_lookup函数,后者会直接使用mask_array中该下标的sw_flow_mask进行查找。否则,则遍历mask_array,依次尝试:
- flow_lookup
/* Flow lookup does full lookup on flow table. It starts with
* mask from index passed in *index.
*/
static struct sw_flow *flow_lookup(struct flow_table *tbl,
struct table_instance *ti,
const struct mask_array *ma,
const struct sw_flow_key *key,
u32 *n_mask_hit,
u32 *index)
{
struct sw_flow_mask *mask;
struct sw_flow *flow;
int i;
if (*index < ma->max) { /// get mask by index
mask = rcu_dereference_ovsl(ma->masks[*index]);
if (mask) {
flow = masked_flow_lookup(ti, key, mask, n_mask_hit);
if (flow)
return flow;
}
}
for (i = 0; i < ma->max; i++) { /// travel all mask in array
if (i == *index)
continue;
mask = rcu_dereference_ovsl(ma->masks[i]);
if (!mask)
continue;
flow = masked_flow_lookup(ti, key, mask, n_mask_hit);
if (flow) { /* Found */
*index = i;
return flow;
}
}
return NULL;
}
- masked_flow_lookup
masked_flow_lookup对sw_flow_key进行掩码计算后,计算hash值,找到对应的bucket,然后遍历链表,依次每个流表项sw_flow进行比较。并返回匹配的流表项。
static struct sw_flow *masked_flow_lookup(struct table_instance *ti,
const struct sw_flow_key *unmasked,
const struct sw_flow_mask *mask,
u32 *n_mask_hit)
{
struct sw_flow *flow;
struct hlist_head *head;
u32 hash;
struct sw_flow_key masked_key;
ovs_flow_mask_key(&masked_key, unmasked, false, mask);
hash = flow_hash(&masked_key, &mask->range); ///mask key -> hash
head = find_bucket(ti, hash); ///hash -> bucket
(*n_mask_hit)++;
hlist_for_each_entry_rcu(flow, head, flow_table.node[ti->node_ver]) { /// list
if (flow->mask == mask && flow->flow_table.hash == hash &&
flow_cmp_masked_key(flow, &masked_key, &mask->range)) ///compare key
return flow;
}
return NULL;
}