问题
最近,业务反映了一个TCP连接容窗口突然异常变小的问题,引起数据传输速度异常之慢,如下:
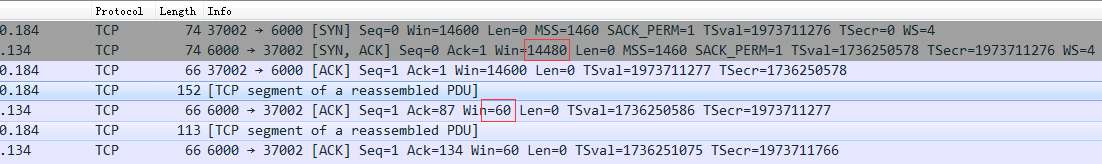
在server端回SYN-ACK包,窗口大小还是144800,在server端确认client的第一个数据包时,一下子变成了60,但数据包的长度只有86个字节。
经过和几位同事的一起各种定位,最终发现是TCP SYN cookies引起的。简单总结一下,以示后人。
TCP引入SYN cookies是为了解决SYN flood问题。
SYN cookie is a technique used to resist SYN flood attacks.The technique’s primary inventor Daniel J. Bernstein defines SYN cookies as “particular choices of initial TCP sequence numbers by TCP servers.” In particular, the use of SYN cookies allows a server to avoid dropping connections when the SYN queue fills up. Instead, the server behaves as if the SYN queue had been enlarged. The server sends back the appropriate SYN+ACK response to the client but discards the SYN queue entry. If the server then receives a subsequent ACK response from the client, the server is able to reconstruct the SYN queue entry using information encoded in the TCP sequence number.
内核参数
- sysctl_max_syn_backlog
sysctl_max_syn_backlog控制Listen Socket的半连接(SYN_RECV)队列长度:
struct inet_connection_sock {
struct request_sock_queue icsk_accept_queue; ////SYN_RECV sockets queue
}
int inet_csk_listen_start(struct sock *sk, const int nr_table_entries)
{
struct inet_sock *inet = inet_sk(sk);
struct inet_connection_sock *icsk = inet_csk(sk);
int rc = reqsk_queue_alloc(&icsk->icsk_accept_queue, nr_table_entries);
///...
sk->sk_state = TCP_LISTEN;
}
int reqsk_queue_alloc(struct request_sock_queue *queue,
unsigned int nr_table_entries)
{
///...
nr_table_entries = min_t(u32, nr_table_entries, sysctl_max_syn_backlog);
for (lopt->max_qlen_log = 3;
(1 << lopt->max_qlen_log) < nr_table_entries;
lopt->max_qlen_log++);
///...
}
static inline int reqsk_queue_is_full(const struct request_sock_queue *queue)
{
return queue->listen_opt->qlen >> queue->listen_opt->max_qlen_log;
}
内核会根据listen的backlog和sysctl_max_syn_backlog计算listen socket的SYN queue的长度。如果队列满了,就会输出下面的日志:
TCP: TCP: Possible SYN flooding on port 6000. Dropping request. Check SNMP counters.
- sysctl_tcp_syncookies
控制是否启动TCP SYN cookies机制。
extern int sysctl_tcp_syncookies;
TCP处理新建连接的逻辑
当接收端收到发送端的SYN包之后,会创建一个request_sock,再给发送端返回SYN/ACK包后,将request_sock加入到LISTEN socket的SYN table:
tcp_v4_do_rcv(TCP_LISTEN) -> tcp_rcv_state_process -> tcp_v4_conn_request:
///ipv4_specific, LISTEN socket handle SYN packet
int tcp_v4_conn_request(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb)
{
struct request_sock *req;
///...
/* TW buckets are converted to open requests without
* limitations, they conserve resources and peer is
* evidently real one.
*/
if (inet_csk_reqsk_queue_is_full(sk) && !isn) { ///SYN queue is full
want_cookie = tcp_syn_flood_action(sk, skb, "TCP");
if (!want_cookie) ///no tcp_syncookies, drop SKB
goto drop;
}
/* Accept backlog is full. If we have already queued enough
* of warm entries in syn queue, drop request. It is better than
* clogging syn queue with openreqs with exponentially increasing
* timeout.
*/
if (sk_acceptq_is_full(sk) && inet_csk_reqsk_queue_young(sk) > 1) {
NET_INC_STATS_BH(sock_net(sk), LINUX_MIB_LISTENOVERFLOWS);
goto drop;
}
req = inet_reqsk_alloc(&tcp_request_sock_ops);
if (!req)
goto drop;
///...
if (likely(!do_fastopen)) {
int err;
err = ip_build_and_send_pkt(skb_synack, sk, ireq->loc_addr, ///send SYN/ACK
ireq->rmt_addr, ireq->opt);
err = net_xmit_eval(err);
if (err || want_cookie) ///tcp_syncookies, don't add to SYN queue
goto drop_and_free;
tcp_rsk(req)->snt_synack = tcp_time_stamp;
tcp_rsk(req)->listener = NULL;
/* Add the request_sock to the SYN table */
inet_csk_reqsk_queue_hash_add(sk, req, TCP_TIMEOUT_INIT); ///Add SYN table
if (fastopen_cookie_present(&foc) && foc.len != 0)
NET_INC_STATS_BH(sock_net(sk),
LINUX_MIB_TCPFASTOPENPASSIVEFAIL);
} else if (tcp_v4_conn_req_fastopen(sk, skb, skb_synack, req)) ///fast open
goto drop_and_free;
///...
}
当接收端再次收到发送端的ACK包时,内核会从SYN table找到与之对应的tcp_check_req,然后创建新的socket,至此,TCP连接算是完成建立(TCP_ESTABLISHED):
tcp_v4_do_rcv(TCP_LISTEN) -> tcp_v4_hnd_req -> tcp_check_req:
static struct sock *tcp_v4_hnd_req(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb)
{
struct tcphdr *th = tcp_hdr(skb);
const struct iphdr *iph = ip_hdr(skb);
struct sock *nsk;
struct request_sock **prev;
/* Find possible connection requests. */
struct request_sock *req = inet_csk_search_req(sk, &prev, th->source,
iph->saddr, iph->daddr); ///get request_sock from SYN table
if (req)
return tcp_check_req(sk, skb, req, prev, false); /// create new socket
///...
}
SYN cookies
在没有开启tcp_syncookies选项时,如果LISTEN socket的SYN queue满之后,会直接丢掉SKB:
///ipv4_specific, LISTEN socket handle SYN packet
int tcp_v4_conn_request(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb)
{
///..
if (inet_csk_reqsk_queue_is_full(sk) && !isn) { ///SYN queue is full
want_cookie = tcp_syn_flood_action(sk, skb, "TCP");
if (!want_cookie) ///no tcp_syncookies, drop SKB
goto drop;
}
开启tcp_syncookies之后,如果LISTEN socket的SYN queue满之后,会创建request_sock,再返给对端SYN/ACK后,并不会将request_sock对象加到SYN queue,而是将其释放:
if (likely(!do_fastopen)) {
int err;
err = ip_build_and_send_pkt(skb_synack, sk, ireq->loc_addr, ///send SYN/ACK
ireq->rmt_addr, ireq->opt);
err = net_xmit_eval(err);
if (err || want_cookie) ///tcp_syncookies, don't add to SYN queue
goto drop_and_free;
这样,当收到对端的ACK后,tcp_v4_hnd_req从SYN queue找不到对应的request_sock对象,就会进入syncookies的处理逻辑:
tcp_v4_do_rcv -> tcp_v4_hnd_req:
static struct sock *tcp_v4_hnd_req(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb)
{
///...
#ifdef CONFIG_SYN_COOKIES
if (!th->syn)
sk = cookie_v4_check(sk, skb, &(IPCB(skb)->opt));
#endif
return sk;
}
cookie_v4_check会检查cookies是否有效,并创建新的request_sock对象,进入正常连接的流程。
SYN cookies与TCP options
对于走SYN cookies逻辑的连接,由于内核没有保存相关socket的状态,所以,SYN包中携带的TCP options就会丢失。
- MSS
接收端在向发送端返回cookies时,会将MSS的值编码到cookies,发送端在返回cookies后,接收端调用cookie_v4_check获取MSS的值:
struct sock *cookie_v4_check(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb,
struct ip_options *opt)
{
///...
if (!sysctl_tcp_syncookies || !th->ack || th->rst)
goto out;
if (tcp_synq_no_recent_overflow(sk) ||
(mss = cookie_check(skb, cookie)) == 0) { ///mss option value
NET_INC_STATS_BH(sock_net(sk), LINUX_MIB_SYNCOOKIESFAILED);
goto out;
}
///...
req = inet_reqsk_alloc(&tcp_request_sock_ops); /* for safety */
if (!req)
goto out;
///...
/* Try to redo what tcp_v4_send_synack did. */
req->window_clamp = tp->window_clamp ? :dst_metric(&rt->dst, RTAX_WINDOW);
///initial window
tcp_select_initial_window(tcp_full_space(sk), req->mss,
&req->rcv_wnd, &req->window_clamp,
ireq->wscale_ok, &rcv_wscale,
dst_metric(&rt->dst, RTAX_INITRWND));
ireq->rcv_wscale = rcv_wscale;
///...
}
- wscale
但是,对于其它option,比如wscale和SACK等信息,就会丢失。后来,又使用timestamp来保存wscale,后来又取消了,参考1,2。详细参考Improving syncookies。
对于TCP SYN cookies的处理逻辑,接收端在收到对端的ACK之后,会重新计算wscale,而不是TCP在建立连接的SYN/SYN-ACK过程协商的wscale,由于wscale的计算受recv buffer等参数的影响,会导致第二次计算的wscale与前面协商的不一致,从而导致发送端和接收端的wscale不一致:
void tcp_select_initial_window(int __space, __u32 mss,
__u32 *rcv_wnd, __u32 *window_clamp,
int wscale_ok, __u8 *rcv_wscale,
__u32 init_rcv_wnd)
{
unsigned int space = (__space < 0 ? 0 : __space); ///sk_rcvbuf size
///...
(*rcv_wscale) = 0;
if (wscale_ok) {
/* Set window scaling on max possible window
* See RFC1323 for an explanation of the limit to 14
*/
space = max_t(u32, sysctl_tcp_rmem[2], sysctl_rmem_max);
space = min_t(u32, space, *window_clamp);
while (space > 65535 && (*rcv_wscale) < 14) {
space >>= 1;
(*rcv_wscale)++;
}
}
而TCP的窗口大小,是受到wscale影响的,从而就会导致出现开头的问题。
总结
这本来是一个很简单的问题,但定位过程却走了不少弯路,从一开始就聚焦于TCP窗口机制,企图从中找问题,而忽略了内核的一些关键输出。再次说明了那个问题:* 表面上复杂的问题,背后的原因都非常简单!*
不管怎样,目前内核的TCP SYN cookies机制是有缺陷的,请慎用。